Article
A brief biography of A.B. Shidlovskii is given at the beginning of the article. Then it tells about the origins of the method - the Hermite and Lindemann theorems. The main definitions and results of the works of K. Siegel in 1929 and 1949 are formulated. The definition of the
𝐸− function and the conditions for the normality of a set of functions are given, examples are given. The story about the works of A.B. Shidlovskii began with the condition of irreducibility of a system of functions. Then the three main theorems of A.B. Shidlovskii and their main consequences are formulated. A theorem on the linear independence of the values of a set of 𝐸−
functions with coefficients from an imaginary quadratic field is presented. A similar theorem is formulated in the case of arbitrary algebraic coefficients. The hypothesis of K. Siegel on the structure of the set of 𝐸− functions satisfying differential equations is formulated and its solution is described. The formulations of theorems are given under which generalized hypergeometric
functions are algebraically independent over the field of rational functions, and their values at algebraic points are algebraically independent. Quantitative problems are described - estimates of measures of linear and algebraic independence of function values. Unimproved estimates are given. Another class of functions is considered, to which the Siegel-Shidlovskii method can be applied, the class of 𝐺− functions. The factorial cancelling condition is formulated, which holds
for all considered 𝐺− functions. The concept of a global relation is given and the possibility of its application to series diverging in the field of complex numbers is described. It describes the arithmetic nature of results of summation of divergent series.
This paper surveys different approaches to explicit formulas for the Hilbert symbol and their generalizations to 𝑝-adic representations in terms of 𝑝-adic Hodge theory.
The paper provides a comprehensive investigation of associated Galois modules and orders for totally ramified extensions of complete discrete valuation fields. The authors focus on explicit computations and systematic construction of bases for these modules, with particular emphasis on elementary abelian extensions of degree 𝑝2. The study introduces and develops the theory of graded-independent sets and diagonal bases, which enable constructive description of the modules 𝛾𝑖 and related associated orders. The central achievement is Theorem 3.3.2, which provides an explicit computation of the modules 𝛾𝑖 for extensions with Galois group (Z/ 𝑝Z)2 and ramification jumps distinct modulo 𝑝2. The paper thoroughly examines properties of the introduced constructions, including their relationship with classical associated orders and the behaviour under tame lifts. The obtained results are generalized to the case of relative associated modules 𝛾0
𝑖 = 𝛾𝑖 ∩𝑘0[𝐺], where 𝑘0 ⊂ 𝑘. The paper extensively utilizes the isomorphism between 𝐾 ⊗𝑘𝐾 and 𝐾[𝐺] constructed by the first author, and presents a detailed analysis of filtrations on tensor squares and their connection to Galois module structure. Respectively, the text can
be interesting to specialists in algebraic number theory and arithmetic geometry.
We give a complete description of the 𝐵𝑉 -structure on the Hochschild cohomology for local algebras of semidihedral type over an algebraically closed field of characteristic 2. In Erdmann’s classification, these algebras are described by a parameter 𝑘. We consider the case of even parameter 𝑘 > 3. The methods of comparison morphisms and contracting homotopies are applied.
Generalized Honda formal groups are the next step in a chain of generalizations the multiplicative formal group – Lubin-Tate formal groups — relative Lubin-Tate formal groups — Honda formal groups. This paper continues the study of properties of this class of formal groups focusing on their homomorphisms. In particular, we show that every homomorphism of generalized Honda formal groups can be expressed as a composition of a chain of distinguished isogenies and an isomorphism. It implies that for any generalized Honda formal group of finite height an isogeny class contains only a finite number of isomorphism classes. The results obtained give an idea of the structure of homomorphisms of formal groups over an arbitrary 𝑝-adic ring
of integers.
This article is devoted to the use of sequences of Artin-Schreier equations to defining 𝑝-Galois extensions of complete discrete valuation fields of mixed characteristic. Along with a review of
known results in this area, some new results for abelian 2-extensions are obtained. Furthermore, the study of almost maximally ramified extensions introduced by S. V. Vostokov in his study of additive Galois modules is continued. It is proved that if the Galois group of such an extension has period p, it is necessarily abelian.
In the present paper we give a new proof of the description of irreducible subgroups generated by root subgroups in special linear group SL(𝑛,𝐾). For the first time such a description was
appeared in J. McLaughlin’s work. His work was one of the first papers dedicated to study of the generations by long root unipotent subgroups in Chevalley groups. At the present time the geometry of long root subgroups is a well-established field. But it remains a lot of unsolved tasks about short root unipotent subgroups. In particular, the description of irreducible subgroups
generated by short root subgroups in exceptional Chevalley groups over arbitrary field is unknown. In our proof we consider the group SL(𝑛,𝐾) as the Chevalley group of type Aℓ. Thus
in our opinion it is possible to use the given approach for study of the irreducible subgroups generated by short root subgroups in Chevalley groups.
This article continues the series of works by the first author on the convergence of sequences and series in multidimensional local and complete fields.
Multidimensional fields are a chain of discretely normalized fields, where each subsequent field is the residue field of the previous one. As a result, the elements are represented as a
series, and when using the standard topology of discrete normalization, the series defining the elements of the field may not necessarily converge. Therefore, on multidimensional complete fields, a complexly constructed Parshin topology is used, taking into account the topologies of the residue fields (see [15], [5], and [6]). In this topology, the series of all elements of the multidimensional field converge. However, another important property is not satisfied in the Parshin topology, which is the convergence of all power series with coefficients from the ring of integers when the element of the maximal ideal is substituted for the variable.
In [9] by the first author the concept of a convergence set is introduced, which is a set such that a series with coefficients from this set converges on a maximal ideal, and a criterion for a
convergence set is proved. In [10], convergence sets are studied using their multi-indices, which form a convergence monoid, and in [8], rings that are convergence sets are constructed and their
properties are studied. In this work, it is shown that the additive shift of a convergence set gives a convergence set, that any convergence set is sequentially closed, and that a convergent sequence always forms a convergence set. These statements provide a convenient sufficient condition for a sequence to
be infinitesimal and allow the construction of a convergence ring that contains the limit of a convergent sequence and all its members.
In the present paper we complete the description of the subgroups generated by a pair of 2-tori in GL(𝑛,𝐾). Recall that 2-tori in GL(𝑛,𝐾) are the subgroups conjugate to the diagonal
subgroup of the following form diag(𝜀, 𝜀, 1, . . . , 1). In work [2] the reduction theorem for the pairs of 𝑚-tori was proved. It follows from it that any pair of 2-tori can be embedded in
GL(6,𝐾) by simultaneous conjugation. The orbit of a pair of 2-tori (𝑋, 𝑌 ) is called the orbit in GL(𝑛,𝐾), if the pair (𝑋, 𝑌 ) is embedded in GL(𝑛,𝐾) by simultaneous conjugation and it can not be embedded in GL(𝑛 − 1,𝐾). It is clear that 𝑛 can take values 3, 4, 5 and 6. In the same work the orbits and spans of 2-tori in GL(6,𝐾) were described. In the subsequent papers we described the pairs of 2-tori in GL(5,𝐾), the orbits of pairs of 2-tori in GL(4,𝐾) and the spans in GL(4,𝐾) corresponding to degenerate cases (the reductive part of the group is not larger than GL(2,𝐾)). In this paper we describe undegenerate cases of pairs of 2-tori in GL(4,𝐾). Thus we complete our description. The most difficult subgroups turns out the groups with a reductive part SL(2,𝐾) × SL(2,𝐾) or SL(2,𝐿), where [𝐿 : 𝐾] = 2.
This paper is devoted to extending the classical Wolstenholme congruence for the central binomial coefficient (︀2𝑝 𝑝 )︀ to the case of a composite number. An extension of Fermat’s little theorem to the composite case is the Gauss congruence, which has a simple combinatorialdynamic interpretation. To extend Wolstenholme’s congruence to the composite case, it is
necessary to use the Jacobsthal congruence. A combinatorial proof of its weakened version is given based on investigation of the orbit lenghts for a suitable action of Sylow 𝑝-subgroups
of the symmetric group.
The space of two-dimensional geometric adeles of a surface is far from being a locally compact space and there is no translation countably additive invariant nontrivial measure on it. At the same time, certain subquotients of the adeles are direct limits of compact subquotients or inverse limits of discrete subquotients, compatible in a special way. Using this fact, the paper defines a translation invariant measure and integration on certain subquotients of the geometric adeles of surfaces. This theory is considerably different from the theory of integration on analytic adeles of surfaces. After revising aspects of one-dimensional theory, the paper includes a full definition of
two-dimensional geometric adeles. A number of their new topological properties are established.
The new translation invariant measure and integration on selective subquotients of the geometric adeles is used for integrals of certain functions in a two-dimensional method describing the size of adelic cohomology groups of surfaces, without using standard adelic complexes. A formula for the Euler characteristic of the surface and its divisor in terms of integrals over subquotients of geometric adeles is proved. Using the Euler characteristic, a new two-dimensional adelic intersection number is introduced. For geometric surfaces it is a positive multiple of the standard intersection number. Several results in the previous study of geometric adeles are given new proofs.
The article proves some variants of the interpolation theorem for the intuitionistic predicate calculus without functional symbols and equality with a special-form interpolant. The most interesting case is the universal Horn interpolant: the axioms of many algebraic systems are given by universal Horn formulas. The results obtained in this work can be useful both from the point of view of proof theory and in applications, for example, when solving problems of artificial intelligence and developing logical programming languages. The article is written in the spirit of proof theory, the main tools are sequential calculus and such techniques for proof transforming as reversing the applications of inference rules, rearranging the applications of rules according to S. K. Kleene and weeding according to V. P. Orevkov.
The article consists of an introduction, the main part divided into 3 paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction contains a brief historical overview and discussion of the relevance of the work. In the first paragraph of the main part, the necessary definitions are introduced and the main result is formulated. The second paragraph is devoted to the description of the version of sequent intuitionistic predicate calculus IGL constructed by V. P. Orevkov. The third one is devoted to the proof of the main theorem. The conclusion contains a discussion of the results obtained and a brief overview of the prospects for further work.
We study the pseudo-Euclidean analogue of the integrable Zhukovsky case for an axisymmetric body. Two essential parameters were found on the multidimensional parameter space, and the separating set was constructed. The bifurcation curve arrangement on the momentum map plane is explicitly described depending on parameter values. Fomenko invariants analogs for non-singular isoenergy and isointegral surfaces are computed. A visualization of the output of the algorithm for constructing labeled graphs for non-singular isoenergetic surfaces is given.
In this article, the occurrence problem in Artin groups with arboreal is solved.
Let 𝑂𝑋𝑌 be a rectangular coordinate system with an integer lattice, 𝐴𝐵 is a segment with integer ends 𝐴 = (𝑞; 0)𝑂𝑋𝑌 = 𝐴(𝑞) and 𝐵 = (0; 𝑝)𝑂𝑋𝑌 = 𝐵(𝑝) such that the decomposition of 𝑝
𝑞 into a continued fraction has the form [0; 𝑎1, 1, 𝑎3, . . . , 𝑎2𝑁′+1], where 𝑎− 1 , 𝑎3, . . . , 𝑎2𝑁′+1, 𝑁′, 𝑝, 𝑞,𝑁′ ∈ N : (= {1, 2, . . .}), moreover, 𝑝 and 𝑞 are mutually simple.
Consider the set S𝐴𝐵 of such unit squares (cells) of this lattice, that the interior of each of them has a nonempty intersection with 𝐴𝐵. The boundary of this set is represented as a union
of polylines S− 𝐴𝐵 and S+ 𝐴𝐵 such that their extreme vertices are the points 𝐴 and 𝐵. Here, the minus index (plus) indicates that S− 𝐴𝐵 (S+ 𝐴𝐵) lies on the left (right) side of the segment 𝐴𝐵
when moving from 𝐴 to 𝐵.
Polyline S− 𝐴𝐵 (S+ 𝐴𝐵)let’s call left (right) (integer) stepwise approximation of the segment 𝐴𝐵 or continued fraction [0; 𝑎1, 1, 𝑎3, . . . , 𝑎𝑁]. For brevity, we will call such polylines marches, and
their horizontal links—steps, vertical ones—heights, which is caused by association with a flight of stairs. The following results were obtained in the work:
1. Formulas for integer approximation of the stucco fraction, both finite and infinite.
2. Algorithmic construction of marches S± 𝐴𝐵, determined by the considered chain fraction. gives their analytical task through the marches of vectors-terms of the second equality:
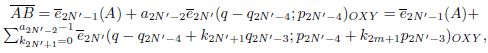
where the vectors 𝑒2𝑁′−1 = (−𝑞2𝑁′−4; 𝑝2𝑁′−4)𝑂𝑋𝑌 and 𝑒2𝑁′ = (−𝑞2𝑁′−3; 𝑝2𝑁′−3)𝑂𝑋𝑌 , whose coordinates are determined by suitable fractions 𝑝𝑛−3/𝑞𝑛−3 of the order 𝑛 = 2𝑁′− − 1.2𝑁′, the original continued fraction, and the points of application of the vectors are indicated in parentheses.
3. The location of the steps of width 𝑎1 in S− 𝐴𝐵, is set using a family of parallel transfers of a segment with ends (𝑞 − 𝑎1; 0)𝑂𝑋𝑌 and (𝑞 − 1; 0)𝑂𝑋𝑌 . We find each member of the family through approximation formulas for [0; 𝑎1, 1, 𝑎3, . . . , 𝑎𝑁].
4. The formula giving the number of steps of width 𝑎1 in S−
𝐴𝐵 is a tridiagonal determinant (2𝑁′ − 5)-th order: the main diagonal consists of elements 𝑎4, 1, 𝑎5, . . . , 𝑎2𝑁′−6,the upper
diagonal is — of ones, the lower one is minus ones, and the rest are zeros.
The notion of a semitransitive binary action of a group 𝐺 on a topological space is introduced. A duality theorem is proved, establishing a bijective correspondence between semitransitive
distributive binary 𝐺-spaces and topological fields whose multiplicative group is isomorphic to 𝐺. This result yields an equivalence between the category of semitransitive distributive binary 𝐺-spaces and the category of topological fields with multiplicative group 𝐺.
As applications of the duality theorem, two important results are established. It is shown that a finite group can act semitransitively, distributively, and binarily only on finite sets whose cardinality is a power of a prime number. A complete characterization of those groups that can appear as multiplicative groups of topological fields is also obtained.
Nonlinear singularly perturbed parabolic equations in domains with angular boundary points are considered. The nonlinear method of angular boundary functions is used to construct the
asymptotics of the solution. It is assumed that in problems determining the main terms of the angular part of the asymptotics of the solution, the nonlinearities are cubic polynomials. The existence of solutions to these problems is based on the method of upper and lower barriers, the construction of which is the main difficulty. In particular, this difficulty is related to the diversity of behavior of cubic polynomials. The paper proposes a classification based on the
allocation of intervals of a certain nature of monotonicity and direction of convexity.
In paper the methodology of concretization of five-constant Murnaghan’s defining relation is described, using the problem of homogeneous uniaxial tension (compression) of a sample
made of a nonlinear elastic material. The methodology is based on the use of experimentally observed values of axial load and transverse elongation of a prismatic sample as a function
of its axial elongation. The experimental curves are approximated by theoretical dependences following from the solution of the tensile-compression problem within the framework of the
considered constitutive relation. Material constants are determined from the requirement of minimal differences between experimental and theoretical data using the least squares method. Аn automated numerical experiment using the python programming language is described. The collected data was used to demonstrate the performance of the proposed concretization of Murnaghan’s defining relation. The numerical experiment was carried out in the local strength analysis package CAE Fidesys. The correctness of the proposed methodology was verified by comparing experimental data and theoretical data obtained for material constants determined within the framework of the presented algorithms for the concretization of the Murnaghan’s defining relation.
The paper presents a lover estimate for the 𝑝-adic value of a polynomial evaluated at polyadic Liouville number.
The paper presents a lover estimate for the 𝑝-adic value of a polynomial evaluated at polyadic Liouville number.
In the article we have for any fixed 𝑐 estimate of 𝜅(𝑐) such that 𝑁 > 𝑁0(𝜀) can be approached by the sum of powers of two primes 𝑝𝑐 1 + 𝑝𝑐 2 by a distance not exceeding 𝐻 = 𝑁𝜅(𝑐)+𝜀, where 𝜀
is an arbitrary positive number. These results were obtained using the density technique developed by Yu.V. Linnik in the 1940s. The density technique is based on applying explicit formulas expressing sums over prime numbers with sums over nontrivial zeros of the Riemann zeta function and using density
theorems that estimate the number of nontrivial zeros of the zeta function lying in the critical strip such that their real part is greater than some 𝜎, 1 > 𝜎 ≥ 1/2.
The results obtained in this paper are based on the application of modern density theorems obtained by A. Ivich. In addition, the proof used the theorem of Baker, Harman, and Pintz: one can approach a given real number 𝑁 > 𝑁0(𝜀) by a prime number by a distance no more than 𝐻 = 𝑁21/40+𝜀. Also, the following result obtained by M. Huxley: |𝜁(1/2 + 𝑖𝑡)| ≪ 𝑡32/205+𝜀.
The paper presents a complete analytical solution to the problem of free vibrations of a string with an arbitrary number of abrupt changes in the wave propagation velocity. A novel combinatorial-analytical method is proposed that allows representing the solution in the form of a compact explicit formula. It is proved that the solution represents a superposition of 2𝑁−1 waves, each corresponding to one of the possible paths of disturbance propagation through the velocity switching moments. It is established that the coefficients in the obtained formula have a clear physical meaning and represent products of transmission and reflection coefficients at the interfaces. The method is generalized to the case of a finite string with zero Dirichlet boundary conditions. The solution is constructed in closed form and confirmed by two independent methods:
the Fourier method and the method of mathematical induction. The obtained results allow analyzing complex wave processes in media with piecewise constant parameters and can be
used in problems of acoustics, seismology, and control theory.
The purpose of this article is to construct a highly accurate and efficient numerical method for studying the dynamics of derivatives of various orders of a singularly perfected differential
equation. In the method of preliminary integration of the highest derivative, the equations and the right part are represented as finite series according to Chebyshev polynomials of the first
kind with unknown expansion coefficients. Before solving the problem, the selected series is pre-integrated and expressions are found in the form of series for all lower derivatives and the
desired solution. Unknown constants appearing during series integration are determined from additional conditions of the problem. Unknown coefficients are determined from a system of
algebraic equations and putting them in the right series, the derivatives and the solution of the problem are calculated.
The article considers a spectral method for evaluating the effective properties of composites and rock samples based on the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). Having limitations on the applied boundary conditions, the method offers high efficiency of stress and strain analysis in a periodic cell due to the asymptotics of FFT in time 𝑂(𝑛 · 𝑙𝑜𝑔(𝑛)). The comparison of the results of homogenization with the Finite Element Method shows the high accuracy of the spectral method in estimating the properties of the rocks. An analysis of the efficiency and convergence of the algorithm for various periodic cells and materials is presented.
Summation of multiplicative functions is found in almost half of the problems of analytical
number theory. The central place in the question of summing the values of multiplicative
functions is occupied by questions about the asymptotic behavior of sums of the form
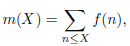
for 𝑋 → ∞, where 𝑓(𝑛) is a multiplicative function of a natural argument. This article is devoted to the study of summation of multiplicative functions over numbers whose prime divisors
lie in specified intervals. An asymptotic formula is obtained for the sums of the product of multiplicative functions whose prime divisors lie in specified intervals.
The problem of finding orbits of the group 𝐺𝐿(𝑉 ) on the space 𝐴𝑙𝑔(𝑉 ) of all bilinear mappings 𝑉 ×𝑉 → 𝑉 is investigated. The work considers only two-dimensional algebras over the field Z2 without using methods of invariant theory. The classification of algebras is considered from new perspectives. To distinguish a large class of algebras, a mapping 𝑃 is used, which naturally arises as a mapping 𝐴𝑙𝑔(𝑉 ) → 𝑉 * × 𝑉 *, assigning to each algebra structure on the space 𝑉 a pair of linear forms 𝑇𝑟1 and 𝑇𝑟2, defined as traces of the left and right multiplication
operators in this algebra. The 𝜏 -action of the group 𝐺𝐿(2,Z2), consisting of non-degenerate square matrices 𝑔, on the set MSC(A) — matrices of structural constants is studied. This action is generally written as 𝜏 : (𝑔,MSC(A)) → 𝑔MSC(A)(𝑔−1)⊗2. The action 𝜏 defines equivalence between matrix operators of two-dimensional algebras and determines the structure for describing action orbits.
For this action, the 𝑃-mapping was used, which has the form 𝑃(𝜏 (𝑔,MSC(A))) == 𝑃(MSC(A))𝑔−1.
For matrix representatives of two-dimensional algebras, a complete matrix classification with various orbits over Z2 is proposed. The connection 𝑃(𝑔MSC(A)(𝑔−1)⊗2) = 𝑒 between MSC(A) and its defining linearly independent system {𝑇𝑟𝑘} = {𝑇𝑟1, 𝑇𝑟2} is presented. This connection of different matrix representatives of orbits equals 𝑞4. The work also addresses the fact that the matrix representatives of the orbits under the action of 𝜏 could potentially intersect; however, the study rigorously proves their non-intersection.
The interrelation in the form of a system of equalities between elements of equivalent orbits of 𝜏 -action by the group 𝐺𝐿(2,Z2) on MSC(A) for further study over fields of higher order is
shown. The results show that the number of different orbits of 𝜏 -action equals 52.
As a consequence in the group-theoretic sense, this problem is equivalent to describing
multiplication on a two-generated abelian group of the form Z2 ⊕ Z2 up to isomorphism.
In conclusion, some properties of the lattice Z𝑞×Z𝑞 (𝑇𝑟𝑘) using the system of vectors {𝑇𝑟𝑘} are given, from which, in particular, follows the description of equivalent matrices with respect
to number by five disjoint linear forms {𝑇𝑟𝑘} = {𝑇𝑟1(MSC(A)), 𝑇𝑟2(MSC(A))} = {𝑇𝑟1(𝐴), 𝑇𝑟2(𝐴)} of the dual space of the algebra A.
Theorems are proved concerning estimates of linear forms in values of generalized hypergeometric series of the form Σ︀∞ 𝑛=0 (𝛼1)𝑛 . . . (𝛼𝑚−1)𝑛 𝑧𝑛, among the parameters of which are transcendental 𝑝-adic Liouville numbers
Mathematics
In this paper, we use statistical compact subspace as a toll to introduce the concept of monotone star s-compact space. This expands upon the work of S.G. Popvassilev, J.E. Porter, M. Matveev, L. Junqueira, R. Wilson, O. Alas, J. van Mill, and V. Tkachuk. Along with a comparison with different forms of compactness, several preservation like properties of monotone star s-compactness are investigated. More over a finite intersection like characterization of the space is established with the help of $\delta_0$-intersection property.
Сomputer science
The phase graphs of semiclassical asymptotics of solutions to the two-dimensional massless Dirac equation with a localized initial condition in a constant (independent of position and time)
electromagnetic field have been studied. The considered equation describes the propagation of quasiparticles (electrons and holes) in graphene, with the electric component of the field parallel to the graphene plane and the magnetic component perpendicular to it. Formulas for the phases have been obtained for all values of the electromagnetic field components.
numerical assessment of the crack resistance of titanium alloy sheet blanks with various microstructures connected by pressure welding in the superplasticity mode is considered. The structural and mechanical model of the object under consideration is represented as a graph.
Based on functional averaging, an iterative method for finding stress and strain parameters for its vertices is implemented as a generalization of Newton’s method. The presented results of
a mathematical analysis of the mechanics of the origin and development of cracks in a twolayer welded billet made of VT6 titanium alloy with a fundamentally different microstructure
indicate the prospects of using such layered titanium compositions in critical products in order to increase their structural strength.
Authors of paper put before themselves a problem: to acquaint the mathematical public with mathematical creativity of some foreigners of graduates of such Russian high schools as Financial
university at the Government of the Russian Federation, the Moscow technical university of communication and computer science, in these educational institutions work authors of the clause. Authors have finished the Tula state pedagogical university of L.N.Tolstoy and should remember foreign graduates of the period of the USSR. Influence of Russian education
on mathematical creativity of foreign graduates of the Russian high schools deserves special attention.
Russia is famous for the achievements in mathematics area, high level of teaching of mathematics. The Russian mathematical formation makes considerable impact on foreign graduates, on the international scientific cooperation. Historical achievements, participation in the international projects, joint projects, publications and teaching behind a boundary-all it promotes strengthening of relations between the Russian and foreign scientists, enriching a world science with new ideas and opening. Some foreign graduates of the Russian high schools have made outstanding career. For example, Hamadun Round worked as the secretary general of International Telecommunications Union, specialised agency of the United Nations, prosecuting subjects of information-communication technologies. In the list of references works of foreign graduates are listed.
The article describes a method for modeling the temperature parameters of laser exposure in the COMSOL software environment (COMSOL Multiphysics PC), which makes it possible
to clean its surface from scale without destroying the surface layer of a steel product, optimize the microstructure and improve the physics-mechanical properties of the working surfaces of
rolled carbon steel.
Based on theoretical concepts of thermal processes that determine the energy and temperature effects of laser radiation, the simulation resulted in the development of equations for the temperature of local heating of the treated surface and the area of radiation coverage per unit time. Using them in a numerical experiment, the characteristics of thermal heating-cooling
cycles during laser scanning were determined during surface cleaning of rolled steel samples of grade 20 from scale consisting of magnetite (Fe3O4). The values of the heating temperatures
of scale and steel during the cleaning process were obtained, and their distribution at different depths of scale and steel was determined during repeated scanning with a continuous laser
beam. A slight accumulation of thermal energy from the nearest thermal cycles (laser scanning passes) was revealed. During all thermal cycles, an increase in the stationary surface temperature
of the samples by only 100 degrees was recorded, which does not affect the structural stability of the steel surface.
The research results served as the basis for the registration of a patent of the Russian Federation for a method of laser micromachining of steels (RU 2 836 694 C1).
The article describes a technique for modeling the energy parameters of laser exposure in the COMSOL software environment (COMSOL Multiphysics PC), which makes it possible
to optimize the microstructure and improve the physics-mechanical properties of the working surfaces of carbon steel parts without destroying the surface layer.
Based on theoretical concepts of the mechanisms of the main processes that determine the energy characteristics of laser radiation exposure, equations of the average energy density
(energy dose) of laser radiation, the temperature of local heating in the center of the scanning spot of the treated surface, as well as the area of radiation coverage per unit time and the rate
of radiation coverage sufficient to change the microstructure of carbon steel without destruction of the surface layer.
Based on their experimental testing, laser exposure modes (microstructuring) were developed, which made it possible to control the diffusion of carbon from the inner layers of the part
to its working surfaces. The implementation of the developed modes made it possible to form the structure of the surface layer with a high carbon content and high hardness without melting
due to the diffusion of carbon from the inner layers to the working surfaces of the products.
The research results served as the basis for the registration of a patent of the Russian Federation for a method of laser micromachining of steels (RU 2 840 325 C1).
Краткие сообщения
This paper develops a program for finding best joint approximations of the second kind for dependent irrationalities.
The results of calculations using the mathcad15 computer mathematics system are presented, confirming the conclusions of [2] that, starting from a certain point, all joint best approximations of the second kind for dependent random variables are determined by the denominators of the convergents of the fundamental irrationality, of which all others are multiples.
In 1963, Hawley [1] (see also [2]), based on estimates of average trigonometric sums from solutions of quadratic comparisons, proved for the first time an asymptotic formula for the average number of divisors of a quadratic polynomial with a power-law decrease in the residual term. These results were later reinforced in [3] and [4]. In the present paper, we prove stronger results on this topic.
This paper studies best simultaneous approximations of the second kind for linearly dependent irrationalities. It is shown that, starting from a certain point, they are determined by the convergents of the first irrationality, of which all others are multiples.
The aim of the work is to construct pseudorandom number generators based on expansions of almost polyadic numbers in powers of a given number. A polyadic number is usually called a
series of the form Σ︀∞ 𝑛=0 𝑎𝑛𝑛!, where 0 ⩽ 𝑎𝑛 ⩽ 𝑛, 𝑎𝑛 is an integer. Series of this type, converging in all fields of 𝑝–adic numbers, except for a finite number of them, having rational coefficients, are called almost polyadic numbers.
We shall assume that 𝜆𝑖 = 𝑎𝑖 𝑏𝑖 , 𝑖 = 1, . . . ,𝑚, where 𝑎𝑖, 𝑏𝑖 are positive integers, N.O.D. (𝑎𝑖, 𝑏𝑖) = 1, 𝑖 = 1, . . . ,𝑚 and 𝜆𝑖 − 𝜆𝑗 ̸∈ Z for 𝑖 ̸= 𝑗. It can be shown that under these conditions the series
Σ︀∞ 𝑛=0 (𝜆𝑖)𝑛(𝑏𝑖)𝑛𝑍𝑛, 𝑖 = 1, . . . ,𝑚 are algebraically independent over the field of rational functions of 𝑧 [1].
This implies the infinite algebraic independence of polyadic numbers Σ︀∞ 𝑛=0 (𝜆𝑖)𝑛(𝑏𝑖)𝑛, 𝑖 = 1, . . . ,𝑚 [2].
It can be assumed that the expansion digits of the partial sums
Σ︀𝑁 𝑛=0 (𝜆𝑖)𝑛(𝑏𝑖)𝑛, 𝑖 = 1, . . . ,𝑚 of the series under consideration have good statistical properties. The article describes the results
of the experiments conducted.
We consider sets of integers 𝑎(𝑘,𝑗) 𝑛 , 𝑗 = 1, ..., 𝑚, 𝑘 = 1, ..., 𝑇𝑗 which satisfy conditions
𝑎(𝑘,𝑗)𝑛 = 𝑎(𝑘,𝑗)𝑛+𝑇𝑗, 𝑗 = 1, ..., 𝑚, 𝑘 = 1, ..., 𝑇𝑗 , 𝑛 = 0, 1, ...
and functions
𝐹𝑗,𝑘(𝑧) =∞Σ︁𝑛=0𝑎(𝑘,𝑗)𝑛𝑛!𝑧𝑛, 𝑗 = 1, ..., 𝑚, 𝑘 = 1, ..., 𝑇𝑗 .
We find conditions under which the set of functions
1, 𝑒𝑧, 𝐹𝑗,𝑘(𝑧), 𝑗 = 1, ..., 𝑚, 𝑘 = 2, ..., 𝑇𝑗
is linearly independent over C(𝑧) and for any rational 𝛾 ̸= 0 their values at 𝛾 are linearly
independent numbers.An estimate of the measure of linear independence of these numbers is
obtained. The result can be used to generate pseudo-random numbers.
In this paper, we use statistical compact subspace as a tool to introduce the concept of monotone star s-compact space. This expands upon the work of S.G. Popvassilev, J.E. Porter, M. Matveev, L. Junqueira, R. Wilson, O. Alas, J. van Mill, and V. Tkachuk. Along with a comparison with different forms of compactness, several preservation like properties of monotone star s-compactness are investigated. More over a finite intersection like characterization of the space is established with the help of 𝛿0-intersection property.






























