Article
Discrete Mathematical Analysis (DMA) is a new approach to data analysis, focused on the
researcher and occupying an intermediate position between hard mathematical methods and soft fuzzy methods.
Fuzzy Sets (FS) play an important role in DMA, some of which are models of discrete
analogs of fundamental mathematical properties (proximity, limit, trend, connectivity, . . .), as well as Fuzzy Logic (FL), which allows combining fuzzy models into data analysis algorithms, in particular, according to classical mathematical scenarios.
In DMA, a regression approach to the limit and derivative is adopted: they are, respectively,
the value and slope of a linear regression, constructed based on a function and fuzzy structure on the initial finite space, modeling the limit transition at its point.
Thus, the regression limit and regression derivative always exist. The question arises about
their quality, in particular, the ability to detect discrete smoothness. This requires a more
in-depth regression analysis than traditional methods, which is the focus of this paper.
For a system of linear algebraic equations (SLAE) 𝐴𝑥 = 𝑏 in a finite-dimensional Euclidean
space 𝐸, a constructive description of the manifold of its solutions Φ(𝐴, 𝑏) is obtained using
the Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization. This description consists of an unconditional linear
parameterization.
This circumstance opens up entirely new possibilities for using SLAEs, as it allows one to
theoretically take into account a priori information about the properties of the true solution
𝑥и in its search on the manifold Φ(𝐴, 𝑏). Technically, this looks like this: the expert opinion
on the solution 𝑥и is formalized by a non-negative functional 𝐹 on Φ(𝐴, 𝑏), and the solution
𝑥и minimizes it. Thanks to the linear parameterization of Φ(𝐴, 𝑏), the minimization of 𝐹 is
unconditional.
The paper pays special attention to the case where expert information about the solution 𝑥и is formally represented by a fuzzy structure 𝜇 of coordinate weights in the space 𝐸, expressing their role in the SLAE 𝐴𝑥 = 𝑏. We call the pair (𝐴𝑥 = 𝑏, 𝜇) a fuzzy SLAE. The formation of its solutions Φ(𝐴, 𝑏, 𝜇) ⊆ Φ(𝐴, 𝑏) is associated with nonlinear optimization, for which polynomial descent algorithms are developed in the paper.
The research results are illustrated with examples.
Multidimensional Hyperbolic-Elliptic Equations describe important physical, astronomical,
and geometric processes. It is known that the oscillations of elastic membranes in space can
be modeled by multidimensional hyperbolic equations based on Hamilton’s principle. Assuming that the membrane is in equilibrium in the bending position, Hamilton’s principle also leads to multidimensional elliptic equations.
Consequently, the oscillations of elastic membranes in space can be described using
multidimensional hyperbolic-elliptic equations.
The problem of the well-posedness of the Dirichlet problem for mixed-type equations in
special domains has been the subject of research by many authors in both two-dimensional and multidimensional cases.
The author previously studied the Dirichlet problem for multidimensional hyperbolicparabolic equations, where the unique solvability of this problem was demonstrated, significantly depending on the height of the considered cylindrical domain.
In this work, a Dirichlet-type problem is studied in a cylindrical domain for a certain class
of multidimensional hyperbolic-elliptic equations, and an explicit form of its classical solution is obtained.
It is shown that the unique solvability depends only on the height of the hyperbolic part of
the cylindrical domain, and a uniqueness criterion for the solution is provided.
The work studies the problem of representing the natural number 𝑛 as the sum of the squares
of four prime numbers from an arithmetic progression. The number of natural numbers that
cannot be represented in the specified form has been estimated, i.e. the exceptional set of the
problem, is estimated.. Also, for the first time, a lower estimate was obtained for the number
of representations of a given non-exceptional 𝑛 in the indicated form.
This work is devoted to the study of singularities of Nijenhuis operators – fundamental
objects of Nijenhuis geometry. Although the Nijenhuis tensor was introduced by Albert
Nijenhuis back in 1951, this field received active development relatively recently thanks to
a series of works by A.V. Bolsinov, A.Yu. Konyaev, and V.S. Matveev.
In dimension two, the classification of linear Nijenhuis operators, operators acting on a
linear space, whose components linearly depend on coordinates, is known. There exists an
important one-to-one correspondence between linear Nijenhuis operators and left-symmetric algebras, which makes their classification an equivalent problem.
Despite its apparent simplicity, the problem remains challenging even for small dimensions
and can be solved only under certain additional constraints. This paper investigates threedimensional linear Nijenhuis operators (or, equivalently, three-dimensional left-symmetric algebras) under the condition of functional independence of the characteristic polynomial coefficients. A complete classification of operators with this additional condition was recently obtained, yielding a list of eight operators.
The main objective of this paper is to study the singularities of such operators. A singular
point is defined as a point in any neighbourhood of which the algebraic type of the operator (Jordan normal form) changes. The paper determines singular points for the considered class of Nijenhuis operators and constructs their sets in three-dimensional space.
In this paper, for 𝑠 ⩾ 3, we describe an algorithm for constructing sequences 𝑃𝐻(𝑠,⃗𝑎,𝑁)𝑖 —
𝑠-dimensional optimal coefficients ⃗𝑎 = (1, 𝑎, 𝑎2 (mod 𝑁), . . . , 𝑎𝑠−1 (mod 𝑁)) modulo N, such
that 𝑎𝑠 ≡ ±1 (mod 𝑁). We construct a sequence such that the error in numerically calculating
the integral of the boundary function of class 𝐸2 𝑠 ℎ(⃗𝑥) = 3𝑠Π︀𝑠 𝑖=1(1 − 2𝑥𝑖)2 over parallelepiped grids 𝑀(⃗𝑎,𝑁) on the cube [0, 1)𝑠 decreases with increasing 𝑁.
The work is devoted to the consideration of multi-qubit and multi-qudit quantum systems
in pure states, their description in terms of partitioning into non-overlapping sets of entangled qubits (qudits) — sets of entanglement, the formula of logarithmic entanglement of multiqubit and multi-qudit quantum systems in pure and mixed states is presented. Using artificial intelligence methods, the classification of multi-qubit systems is made, taking into account the maximum instantaneous entanglement value and logarithmic entanglement, diagrams of the distribution of these characteristics depending on the factorization of the system state vector into sets of entanglement are constructed. A formula for the ensemble-averaged logarithmic entanglement for multi-qubit and multi-qudit quantum systems in pure states has been constructed.
Gelfond obtained a result on the uniform distribution of sums of digits of 𝑏-ary expansions
of natural numbers over residue classes modulo 𝑑 for an arbitrary 𝑑. Later, Lamberger and
Thuswaldner, using deep estimates of trigonometric sums, obtained an analogue of Gelfond’s theorem, in which instead of 𝑏-ary expansions, expansions over linear recurrent bases satisfying the Parry condition and some additional condition on the coefficients, are used. In this paper, we give a new, simpler and self-contained, proof of the Lamberger-Tkuswaldner theorem. Our proof is purely combinatorial and require only Parry condition. In addition, we give a quite simple explicit formula for the exponent in the remainder term. In contrast to the Lamberger-Thuswaldner result, obtained exponent depends only on 𝑑 and the order of the linear recurrent sequence, but not on its coefficients. However, our result does not include the equidistribution of the sums of the digits modulo 𝑑 of natural numbers running from an arbitrary arithmetic progression, which was also proved by Lamberger and Thuswaldner.
At the end of the paper, some unsolved problems are briefly discussed.
Determining the completeness of finite subsets is an important task in the study of functional systems. In the class of finite automata with composition operations, the problem of checking the completeness of finite subsets is algorithmically undecidable. Conversely, in the class of finite automata with superposition operations, no finite complete systems exist. The subclass of definite automata is notable for having finite complete systems with respect to superposition operations; however, the problem of verifying the completeness of finite subsets in this case is also algorithmically undecidable. Previously, the class of linear automata with composition operations was studied, and an algorithm for determining the completeness of finite subsets was developed for this class. At the same time, it was shown that finite complete systems do not exist in the class of linear automata with superposition operations. Of particular interest is the investigation of this problem in the context of definite linear automata with superposition operations. In this work, an algorithm is proposed for verifying the completeness of finite subsets that include the zero constant in the class of definite linear automata.
For the number of zeros of the Riemann zeta-function 𝜁(𝑠) in narrow rectangles of the critical
strip (Re 𝑠 ⩾ 𝛼 ⩾ 0.5 and 𝑇 < Im𝑠 ⩽ 𝑇 + 𝐻), assuming
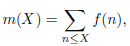
where (𝜅, 𝜆) is an arbitrary exponent pair, 𝜀 < 10^(−4) is any fixed positive number, and
𝑇 ⩾ 𝑇0(𝜀) > 0, an estimate of the form
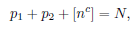
is obtained. Here 𝑎 = 2, 4 and 𝑐 = 172 when 1/2 ⩽ 𝛼 ⩽ 2/3 or 5/6 ⩽ 𝛼 ⩽ 1, and respectively 𝑎 = 8/3 and 𝑐 = 50 when 2/3 < 𝛼 < 5/6 .
For 𝐻 ⩾ 𝑁1−^(1/2𝑐) (ln𝑁)^2, where L = ln𝑁 and 𝑐 is a fixed non-integer number satisfying
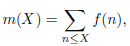
we obtain an asymptotic formula for the number of representations of a sufficiently large integer 𝑁 in the form
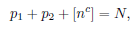
where 𝑝1, 𝑝2 are prime numbers, 𝑛 is a natural number, and
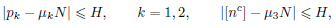
with 𝜇1, 𝜇2, 𝜇3 being fixed positive constants satisfying 𝜇1 + 𝜇2 + 𝜇3 = 1.
In the article, on the class K^0 of infinite binary sequences without the runs of ones, a
consistent probability distribution P is constructed which is induced by a time-homogeneous
Markov chain with a one-step transition matrix P𝜑 , and is completely determined by the
golden ratio 𝜑. Using a Markov chain to construct a probability measure P allows us to apply
Kolmogorov’s existence theorem. The asymptotic distribution of the subclass K^0 of infinite
binary sequences without the runs of ones starting with zero coincides with the analogous
asymptotic distribution of the classical equiprobable scheme . And in this case, the asymptotic
distribution of the class K 0 coincides with the probability P(K^0).
In paper we consider the problem of finding the number of natural numbers that do not
exceed a given 𝑛, satisfying certain conditions for the function 𝜈(𝑚) – the number of prime
divisors of 𝑚. This work summarizes the result of M. V. Leveque, who considered the values
of the function 𝜈 at consecutive terms of the natural series. In contrast, the present article
examines the behavior of this function at consecutive points of an arithmetic progression. The
solution relies on coprimality and the resulting statistical independence of the prime divisors of neighboring terms in the arithmetic progression.
The work is concerned with studying the integration of the Harry Dym equation with the
self-consistent source. The source consists of the combination of the eigenfunctions and linear independent solution with the same eigenfunctions of the corresponding spectral problem for the string equation which has not spectral singularities. While considering the source, the points of the discrete spectrum of the string equation have been as the functions of time. Deduced the time performance of the scattering data of the string equation which allows to integrate the Cauchy problem for the Harry Dym equation with the special self-consistent source in the class of the rapidly decreasing functions via the inverse scattering method.
This article shows that there is a direct connection between the actions of the symmetric
group 𝑆𝑛 on the set of linear Diophantine equations and on the set of their solutions.
Thus, it was found that for coefficients rearrangement in a linear Diophantine equation the
coordinates of its general solution vector are rearranged in the same order, and for variables rearrangement we get the reverse order of the vector coordinates.
There is a similar connection between the actions of the group of the automorphisms of the
integers on the set of linear Diophantine equations and their solutions: if on changes the signs of some coefficients in the equation, then the signs of the corresponding coordinates of the general solution vector are changed too.
We also obtained results on the connection of different actions of the symmetric group on
the set of linear Diophantine equations. For example, rearrangement of the equation coefficients is equivalent to rearrangement of its variables in the reverse order.
Established connections between the actions make it possible to quickly find solutions of an
entire class of linear diophantine equations from a solution of only one of its elements. In turn, studying the actions of other groups on the given set and the connections generated by them would expand this class.
Сomputer science
Two-constant forms of relationships between stresses and strains in nonlinear-elastic isotropic materials are presented. Such materials can be used to dampen vibrations in building structures under dynamic loads (earthquakes, shock waves from explosions). The free energy of the considered relationships is represented as a function of algebraic invariants of the Cauchy-Green strain tensor or natural invariants of the “left” Hencky strain tensor. A method for determining the constants of the presented relationships between stresses and strains has been developed. The proposed method is based on the analysis of experimental dependencies of circumferential deformations on the outer and inner surfaces on the applied internal pressure and solutions to the Lam´e problem for a hollow cylinder in a flat deformed state. It is shown that the present constitutive relationships can be particularized by identifying the linear section of the experimental dependencies and constructing theoretical dependencies under the assumption of small deformations. Thus, the data following the linear section can be used to specify the third-order elasticity moduli of the determining relations constructed on the basis of those considered. Consequently, the methodology presented in the work can also be considered as a partial solution to the problem of particularization the relationships between stresses and strains, including third-order elasticity moduli. For the experimental data presented, it is shown that the results of particularization according to the proposed method correspond to the elasticity moduli determined by means of a classical tensile experiment. The presented method can be used both directly and for the purpose of minimizing the number of experiments in the tasks of particularization the constitutive parameters of nonlinear elasticity theory.
In paper the problem of diffraction of a cylindrical harmonic sound wave on an inhomogeneous liquid spheroid with an absolutely rigid spherical inclusion is considered.
It is assumed that the square eccentricity of the spheroid is a small value. The spheroid
is placed in an infinite homogeneous incompressible ideal liquid. A linear source generating
sound waves is parallel to the axis of rotation of the spheroid. The material of the spheroid
is characterized by variable density and speed of sound which are continuous functions of the radial coordinate.
An approximate analytical solution is obtained by the perturbation method problems with
using decompositions in a row by spherical wave functions.
The results of numerical calculations of the directional patterns of the scattered acoustic
field in the far zone are presented.
Краткие сообщения
In this paper in the model situation the generalized solution of the Cauchy problem of
linearalized the Corteveg – de Vriz equation are investigated. The solution are represented as
the Vinogradov’s trigonometric series, that permits to reduce the deduction to the Vinigradov’s method of the H.Weyl’s trigonometric sums.
This work is devoted to studying the properties of the method of the constructed function
𝜙𝜎(𝑦, 𝑥), which is defined in the infinite domain D of three-dimensional Euclidean space. In this
work, we prove results that allow us to assert the boundedness of a biharmonic function inside
a certain three-dimensional region if it is bounded with its normal derivative at the boundaries
of this region.
This work addresses the problem of finding a stationary Markov chain with maximum
entropy on the set of infinite binary sequences that forbid three consecutive ones. A connection is established between this problem and the non-integer base numeration system studied by A.
O. Gelfond. A probabilistic interpretation of Gelfond’s distribution of remainders is provided
in terms of a three-state ergodic Markov chain. As the main result, the parameters of the
extremal chain are explicitly determined. It is shown that the transition probability matrix and the stationary distribution are expressed via the root 𝜃 > 1 of the equation 1 = 𝜃−1+𝜃−2+𝜃−3.
The entropy of the resulting chain equals ln 𝜃, which defines the maximum achievable entropy in the class of sequences with this forbidden pattern.
A linear space of operator fields that consists of Nijenhuis operators is called a Nijenhuis
pencil. Maximal (by inclusion) Nijenhuis pencils serve as interesting examples of such pencils.
The case when maximal Nijehuis pencil contains a subpencil of symmetric constant (𝑛 × 𝑛)-
matrices (in some fixed coordinate system) was recently investigated in paper [4], in which the
complete description of such maximal pencils was obtained for 𝑛 ⩾ 3. As it turned out, the case 𝑛 = 2 requires special research. This problem is solved in the present paper.






























